In the complex realm of logistics, compliance is the bedrock upon which successful freight brokerage operations stand. Understanding and adhering to the myriad regulations, licensing requirements, and industry standards is not just essential; it’s non-negotiable. Freight brokerage compliance training plays a pivotal role in equipping professionals with the knowledge and expertise to navigate this intricate landscape effectively. In this article, we’ll explore the significance of freight brokerage compliance training, shedding light on how it ensures adherence to legalities, instills best practices, and fosters a culture of integrity within the industry.
- The Crucial Role of Compliance in Freight Brokerage
Compliance is the foundation of trust and reliability in the freight brokerage industry. It ensures that brokers operate legally, maintain ethical standards, and uphold the integrity of the logistics process. Non-compliance can lead to legal repercussions, financial losses, and damage to reputation. - Why Freight Brokerage Compliance Training Matters
Freight brokerage compliance training is designed to educate professionals about legal requirements, industry regulations, and ethical guidelines. By fostering a deep understanding of compliance, it empowers brokers to make informed decisions, reduce risks, and uphold the highest standards of professionalism. - Key Aspects Covered in Compliance Training
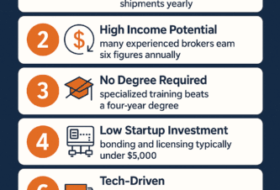
a. Licensing and Regulatory Requirements
Compliance training covers the process of obtaining and renewing licenses, permits, and bonds. It educates brokers about the legal obligations associated with operating as a freight broker, ensuring they fulfill all regulatory requirements.
b. Ethical Practices and Code of Conduct
Ethical behavior is paramount in freight brokerage. Training programs emphasize ethical practices, honesty, transparency, and the importance of maintaining a strong code of conduct when dealing with clients, carriers, and industry partners.
c. Data Security and Confidentiality
With the increasing reliance on digital systems, compliance training addresses data security protocols and confidentiality requirements. Brokers learn how to safeguard sensitive information, ensuring client data remains secure and protected.
d. Handling Industry-specific Challenges
Different industries pose unique challenges. Compliance training equips brokers with industry-specific knowledge, enabling them to navigate challenges related to specialized cargo, regulations, and documentation specific to certain sectors.
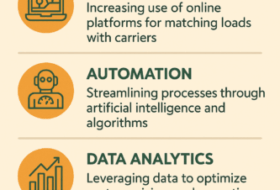
e. Technology Integration for Compliance Management
Training programs introduce brokers to compliance management software and tools. These technologies help automate compliance processes, track regulatory changes, and ensure brokers stay up-to-date with the latest legal requirements.
- Licensing and Regulatory Requirements
Compliance training outlines the procedures for obtaining the necessary licenses and permits to operate legally. Brokers learn about the application process, documentation requirements, and the importance of maintaining up-to-date licenses to avoid legal complications. - Ethical Practices and Code of Conduct
Ethical practices, including fair dealing, honesty, and integrity, are core components of compliance training. Brokers understand the significance of adhering to ethical standards, building trust with clients and carriers, and upholding the reputation of the brokerage firm. - Data Security and Confidentiality
Compliance training educates brokers on data security measures, emphasizing the importance of protecting sensitive information such as client details, financial records, and transaction data. Brokers learn to implement encryption, secure communication channels, and follow data protection laws to safeguard confidentiality. - Handling Industry-specific Challenges
Different industries have unique compliance requirements. Training programs provide insights into industry-specific challenges, such as hazardous materials regulations, perishable goods handling, or international trade laws. Brokers gain specialized knowledge to navigate these complexities effectively. - Technology Integration for Compliance Management
Compliance management software and tools are invaluable assets in ensuring adherence to regulations. Training programs introduce brokers to these technologies, teaching them how to use automation for license renewals, compliance tracking, and staying updated with regulatory changes in real-time. - Continuous Compliance: The Role of Audits and Updates
Compliance is an ongoing process. Training programs emphasize the importance of regular audits and updates. Brokers learn how to conduct internal audits, identify compliance gaps, and implement corrective actions. Additionally, they stay informed about industry updates, ensuring they adapt to new regulations promptly. - Conclusion: Upholding Excellence Through Compliance Training
In conclusion, freight brokerage compliance training is not just a legal requirement; it’s a commitment to excellence. By investing in comprehensive compliance education, brokers ensure the integrity of their operations, gain the trust of clients and carriers, and foster a culture of professionalism within the industry. Upholding compliance standards is not just a responsibility; it’s a testament to a broker’s dedication to ethical conduct and client satisfaction. By embracing compliance training, brokers pave the way for a successful, trustworthy, and reputable freight brokerage career.
Growth + Change = Opportunity! How are you going to capitalize on the opportunity as a freight broker, agent, dispatcher or box truck carrier?